Appearance
Web 页面元素 XPath 定位教程
1. XPath 概述
XPath (XML Path Language) 用于在 XML/HTML DOM 中查找节点。浏览器开发者工具 Elements 面板中结构即 DOM。常见用途:RPA 自动化、UI 测试、爬虫定位元素。
两类:
- 绝对路径:从根节点 html 开始,脆弱:/html/body/div/ul/li[2]/a
- 相对路径:以任意节点为起点,更常用://div[@class='nav']//a[text()='登录']
1.1 从浏览器中获取元素xpath
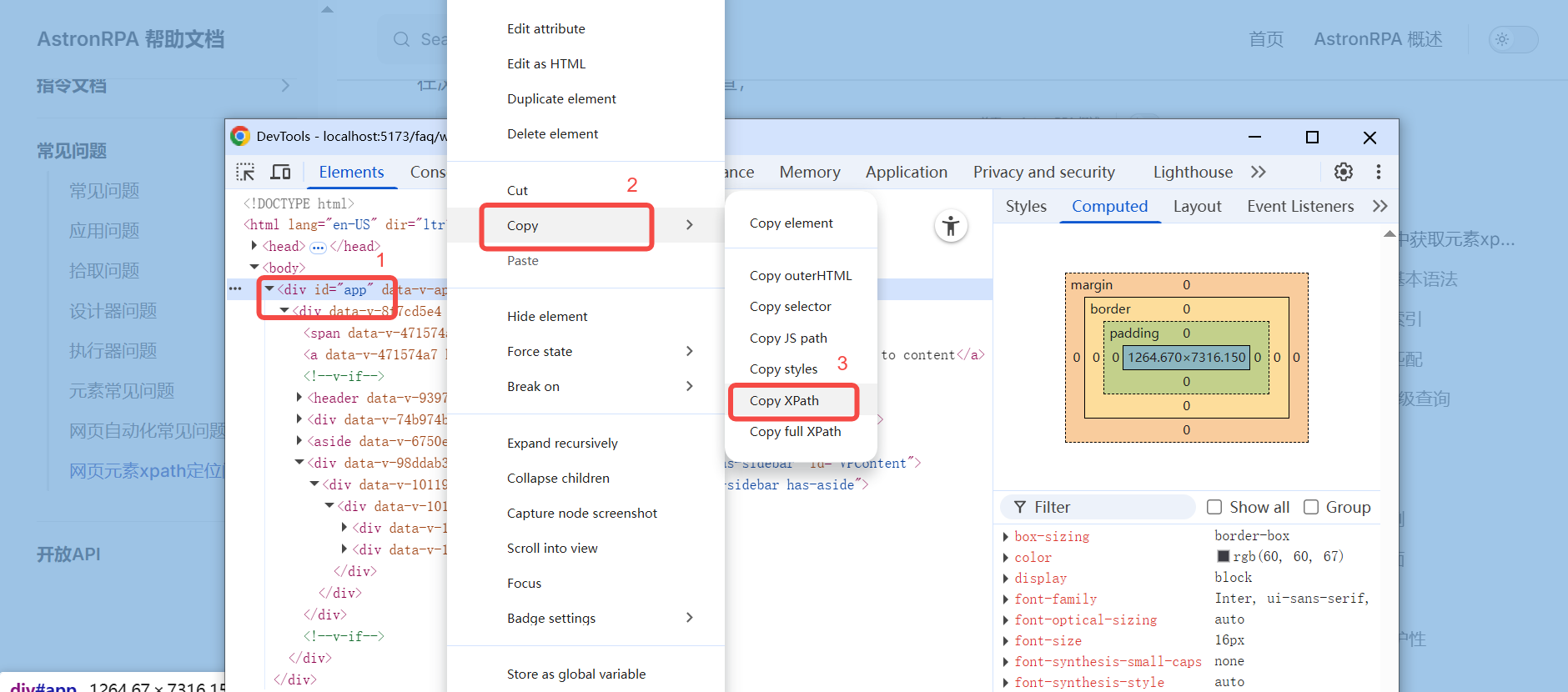
在浏览器网页中点击右键,选择检查,后点击到自己想要检查的元素,右键打开面板,选择copy, 再选择copy xpath 即可获取到对应的xpath //*[@id="app"], 也可选择copy full xpath即全部路径 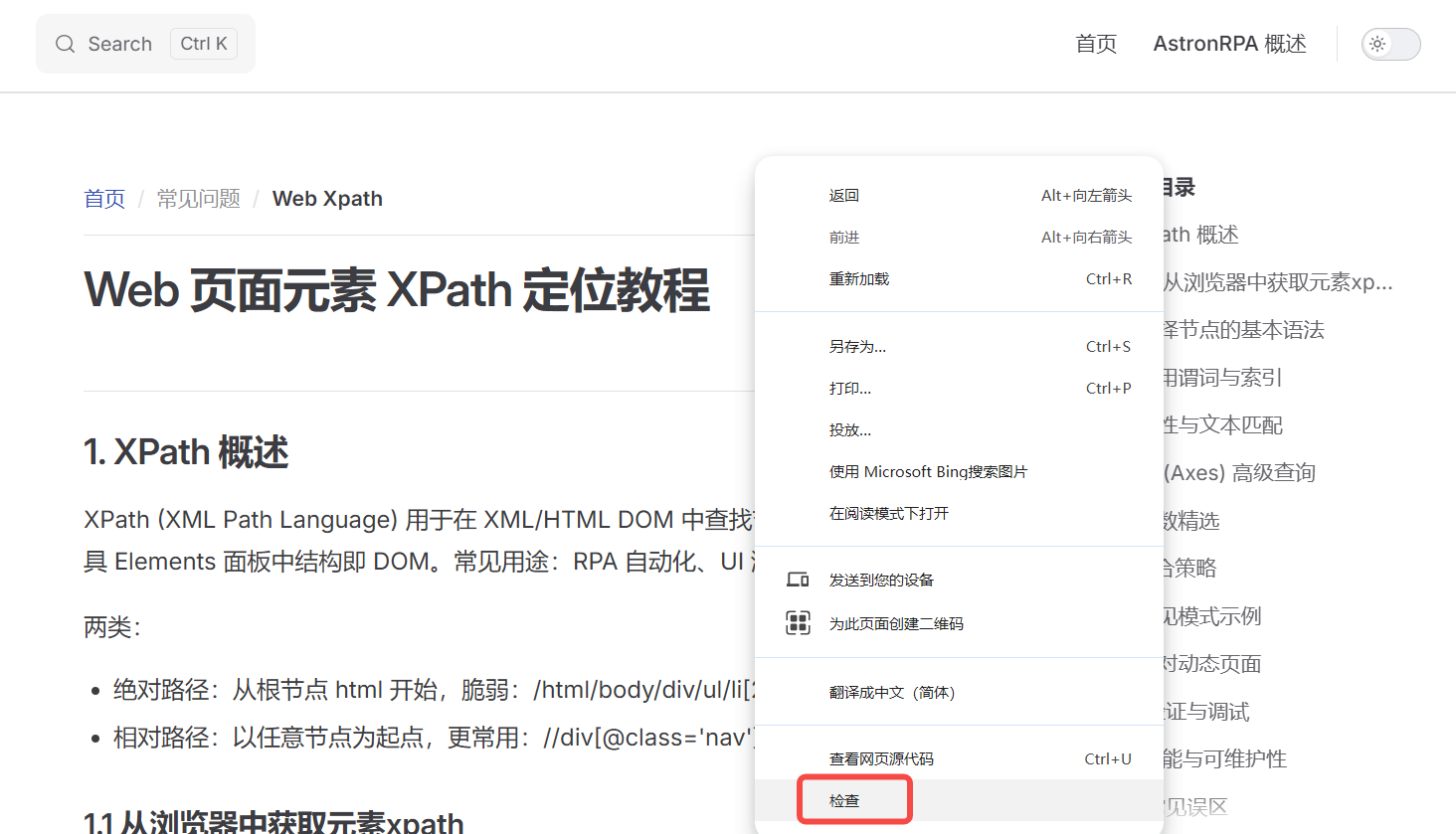
2. 选择节点的基本语法
- // 任意层级向下查找
- / 直接子节点
- . 当前节点
- .. 父节点
- @ 属性
- * 通配任何标签
- | 结果合并 (联合选择)
示例:
- //input[@name='q']
- //ul/li[1]
- //div/*/span
3. 常用谓词与索引
谓词 [] 用于过滤:
- [1] 第一个匹配 (注意 XPath 索引从 1 开始)
- [last()] 最后一个
- [position()=2] 第 2 个
- [@id='kw'] 属性等于
- [@class] 存在该属性
- [@class='a b'] 精确匹配(注意 class 顺序与空格)
- [contains(@class,'btn')] 包含子串
- [starts-with(@id,'user_')]
示例://table[@id='userTable']//tr[position()>1]
4. 属性与文本匹配
- 精确文本://a[text()='提交']
- 文本包含://span[contains(text(),'错误')]
- normalize-space 去除前后空白://div[normalize-space(text())='首页']
- 多层文本:使用 . 获取后代纯文本://div[contains(.,'欢迎使用')]
5. 轴 (Axes) 高级查询
语法:轴名称::节点测试
常见轴:
- ancestor::div 祖先 div
- ancestor-or-self::
- parent::
- child::li
- following-sibling::li 后面同级
- preceding-sibling::li 前面同级
- following::a 文档流中后续任意 a
- preceding::a
- descendant::span
- self::a
组合示例:
- //label[text()='邮箱']/following-sibling::input
- //input[@id='pwd']/ancestor::form
- //li[@class='active']/preceding-sibling::li[last()]
6. 函数精选
- contains(attr,'x')
- starts-with(attr,'x')
- ends-with(attr,'x') (XPath 2.0;浏览器原生多为 1.0,慎用)
- not(condition)
- string-length(text())
- position()
- last()
- normalize-space()
- concat('a','b')
- matches() (XPath 2.0 正则,Selenium 默认不支持)
示例://input[@type='text' and not(@disabled)]
7. 组合策略
- 先锁定局部容器://div[@id='main'] 替代全局搜索
- 再缩小范围:添加 class、data-*、角色属性
- 使用文本或唯一业务属性 (data-test, aria-label)
- 回避易变样式类名 (如自动生成 hash)
- 避免纯索引链://div[3]/ul/li[7] 不稳定
- 用 contains 拆解多类名:contains(@class,'btn-primary')
- 当 id 唯一时优先使用://*[@id='loginBtn']
8. 常见模式示例
- 根据标签与属性://button[@type='submit']
- 模糊 class://div[contains(@class,'dialog')]
- 复合条件://input[@type='password' and @name='pwd']
- 文本 + 结构://h2[normalize-space(.)='用户列表']/following::table[1]
- 兄弟节点://td[text()='价格']/following-sibling::td[1]
- 父子联动://div[@class='item' and .//span[text()='折扣']]
- 部分动态 id://input[starts-with(@id,'user_')]
9. 针对动态页面
- 避免绝对路径
- 不依赖随机数或构建后缀 (如 id='el_169312')
- 定位稳定语义属性:data-testid, data-role, aria-label
- 若 class 多变化,优先使用文本或层级关系
- 可先找外层可识别块再向内://section[@aria-label='搜索']//input[@name='q']
10. 验证与调试
浏览器开发者工具 Console 输入: $ x = $x("//input[@name='q']") (Chrome 支持 $x) $ x[0] 取第一个结果
Selenium 检查: driver.findElement(By.xpath("//a[contains(@href,'/login')]"))
逐步收缩:先 //a 再加属性,再加层级。
11. 性能与可维护性
- 减少前导 // 全局扫描,优先限定起点://main//a
- 避免 descendant 深层过宽://div//span 换为具体结构
- 尽量使用唯一标识,降低结果集合规模
- 团队统一命名 data-* 测试属性
12. 常见误区
- class 多值精确匹配失败:class="a b" 需完整匹配或 contains
- text() 只取直接子文本,嵌套标签需用 . 或 normalize-space(.)
- 误用索引 0(XPath 起始 1)
- ends-with 在 XPath 1.0 不可用
- 过度依赖位置索引易碎
- 使用 //* 无限制扫描导致性能差
13. 推荐优先级 (稳定性由高到低)
- 唯一 id / data-* 属性
- 业务语义属性 (aria-label, title, alt)
- 稳定文本 (少变化语言)
- 局部容器 + 精准属性组合
- 层级 + 兄弟关系
- 索引 (最后手段)
14. 快速模板
- 按文本按钮://button[normalize-space(.)='提交']
- 输入旁标签://label[.='手机']/following::input[1]
- 表格列单元格://table[@id='t']//tr/td[3]
- 下拉选项://select[@name='country']/option[@value='CN']
- 图标按钮://button[.//svg and contains(@class,'close')]
15. 编写步骤建议
- 观察 DOM 结构,找最小稳定包裹容器
- 判断是否有唯一属性
- 选择是否使用文本配合
- 评估未来是否变化 (class 风险)
- 写出初稿,测试 $x 验证数量
- 若返回多个,继续加限定条件
- 确认在不同状态 (加载后/展开后) 一致
- 归档到定位库并注明意图
16. 快速对照速查
- //tag
- //*[@attr='v']
- //*[contains(@attr,'v')]
- //*[starts-with(@attr,'v')]
- //*[text()='v']
- //*[normalize-space(.)='v']
- /ancestor::div
- [position()=n]
- [last()]
- [not(@disabled)]
17. 何时不宜用 XPath
- 简单唯一 id 用 CSS: #loginBtn
- 仅按 class 且无复杂层级:.btn.primary
- 性能极敏场景,CSS 选择器通常更快
但 XPath 在:
- 复杂文本匹配
- 逆向(找父/祖先)
- 兄弟关系
- 组合复杂过滤 更具优势。
18. CSS 对比速览 (参考)
XPath: //div[@id='main']//a[text()='首页'] CSS: #main a:contains('首页') (标准 CSS 不支持文本,需要 JS 扩展;此处说明 XPath 优势)
19. 最终检查清单
- 唯一性:结果数量 = 1 ?
- 稳定性:刷新/切换数据仍成立?
- 可读性:同事可理解意图?
- 语义性:避免 magic number 索引?
- 性能:避免全局暴力扫描?
需要更多帮助?
如果您的问题未在此找到答案,请联系技术支持或查看官方文档获取更多帮助。